Radians
Radians are one way of calculating angles.
There are 4 common ways:
- Radians
- Degrees
- Gradians (basically, 360 degrees = 400 gradians)
- turns - 360 degrees = a turn
From this, we can see that the most complicated type, is in fact, radians.
A radian is the ratio between the length of an arc and it's radius.
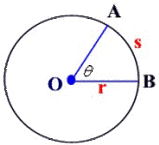
i.e. ----------> length of subtended (by radius) arc / radius ---------------> s / r in the diagram below)----------------------> gives us radians
Hence, you get 1 radian or "1 rad" when length of subtended arc = radius
There are 4 common ways:
- Radians
- Degrees
- Gradians (basically, 360 degrees = 400 gradians)
- turns - 360 degrees = a turn
From this, we can see that the most complicated type, is in fact, radians.
A radian is the ratio between the length of an arc and it's radius.
i.e. ----------> length of subtended (by radius) arc / radius ---------------> s / r in the diagram below)----------------------> gives us radians
Hence, you get 1 radian or "1 rad" when length of subtended arc = radius
From the picture,
We see that s is the subtended arc and AO and BO subtend it. That's what subtend means... to like erm... "mark the boundary of"
When s = r, s/r = r/r = 1 radian
Now, many people say that 2pi = 360 degrees in trigonometry. But why is this so?
This is explained by the derivation or radians.
We see that s is the subtended arc and AO and BO subtend it. That's what subtend means... to like erm... "mark the boundary of"
When s = r, s/r = r/r = 1 radian
Now, many people say that 2pi = 360 degrees in trigonometry. But why is this so?
This is explained by the derivation or radians.
Take a look at the diagram again. Notice that the angle controls the size of s, the subtended arc.
When tita, the angle is bigger, s is also bigger. When tita is smaller, s will also be smaller. The angle and subtended arc are thus proportional.
Think about it this way,
when tita is 90 degrees, AOB will be a quarter-circle --- making s a quarter of the total circumference.
Let's jump a bit here.
When tita, the angle is bigger, s is also bigger. When tita is smaller, s will also be smaller. The angle and subtended arc are thus proportional.
Think about it this way,
when tita is 90 degrees, AOB will be a quarter-circle --- making s a quarter of the total circumference.
Let's jump a bit here.
By definition,
Since 2(pi)r = circumference of a circle, where according to the diagram, tita = 360. Here, we see that y = 2(pi)r
2(pi)r / r radians = 2(pi) radians
Therefore, 2(pi)radians = 360 degrees.
Dividing 2(pi) on both sides gives
1 radian = 360/2(pi) = 180/pi
Hence,180 = pi, 360 = 2(pi)
Since 2(pi)r = circumference of a circle, where according to the diagram, tita = 360. Here, we see that y = 2(pi)r
2(pi)r / r radians = 2(pi) radians
Therefore, 2(pi)radians = 360 degrees.
Dividing 2(pi) on both sides gives
1 radian = 360/2(pi) = 180/pi
Hence,180 = pi, 360 = 2(pi)